In safeguarding critical equipment and ensuring security across diverse locations, device cells, function zones, and factory sites within your automation network, an integrated "defense-in-depth" strategy is pivotal. This cybersecurity approach encompasses physical, technical, and administrative controls. Firstly, establish physical controls via network segmentation, delineating distinct segments. Secondly, enforce technical controls through robust network traffic security and data packet filtering. Lastly, enhance administrative security by adeptly managing IP addresses and enforcing stringent security policies. The utilization of secure routers and firewalls is a paramount step in achieving comprehensive network cybersecurity. Yet, when seeking the ideal router or firewall for your industrial context, what key criteria should you prioritize? This guide provides valuable insights.
Critical Inquiry: Safeguarding Industrial Automation Networks
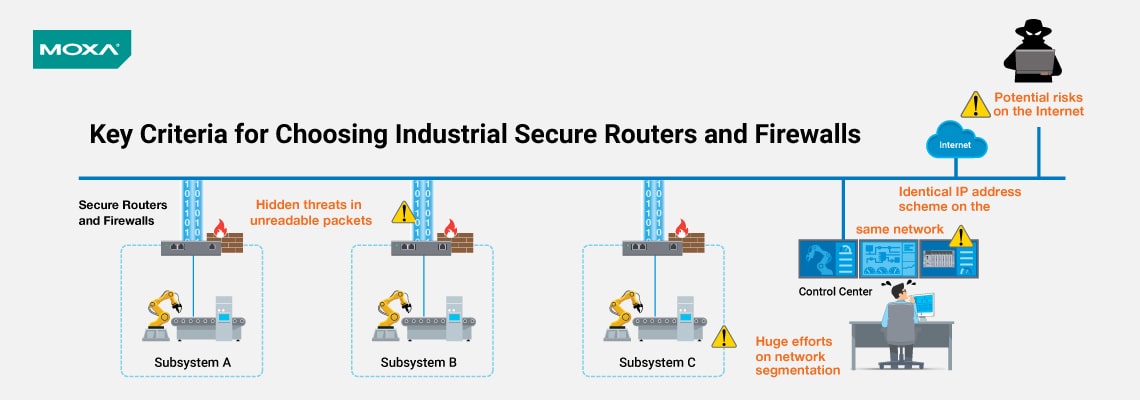
Elevating security within your industrial
automation network has transcended optional status; it's now a mandatory
imperative. The question arises: how can you shield your business and valuable
assets from cyber threats while maintaining uninterrupted industrial
operations?
Key Criteria 1
Integrating Firewalls Seamlessly into Your Network
Incorporating firewalls into your network
doesn't necessitate an overhaul. Network segmentation involves dividing your
network into physical or logical zones using industrial firewalls. These access
control devices scrutinize IP packets, comparing them against preset policy
rules, and determining whether to permit, reject, or enact an alternative
action on the packet.
Firewalls typically fall into two categories: "routing" or "transparent," the choice dependent on application demands. Transparent firewalls stand out in this context. They allow you to retain the same subnet, simplifying firewall integration into an existing network. Notably, transparent firewalls maintain network topology, making them optimal for shielding crucial devices within a control network. Importantly, these firewalls don't require IP subnet reconfiguration as they don't partake in the routing process.
Key Criteria 2
Detecting Threats and Safeguarding Critical Data
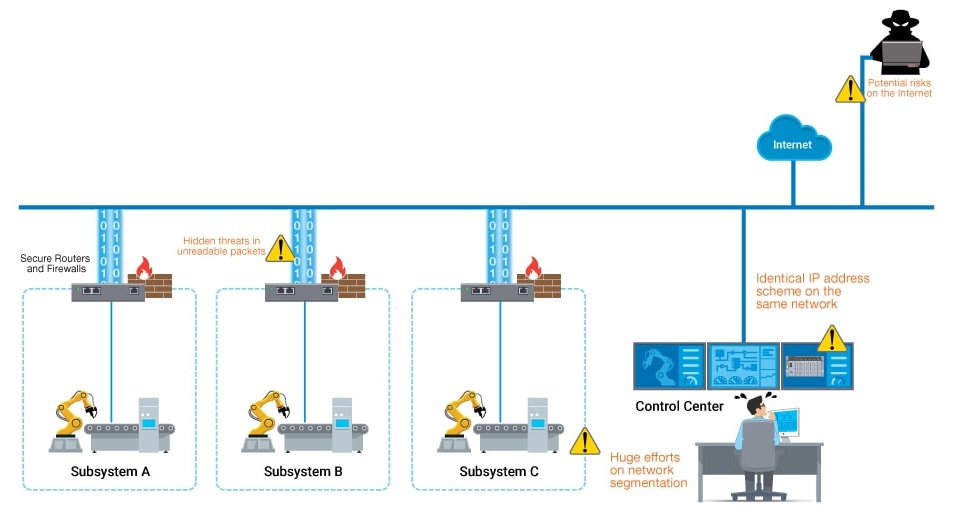
Visualize firewalls as vigilant
gatekeepers. Yet, resolute intruders might find a way through the gates of a
segmented network. This necessitates continuous scrutiny of the traffic
coursing through the established gates. A strategy for achieving this involves
sieving out unwanted commands, such as writing or configuring commands, which
could disrupt industrial processes or trigger unnecessary safety states during
production.
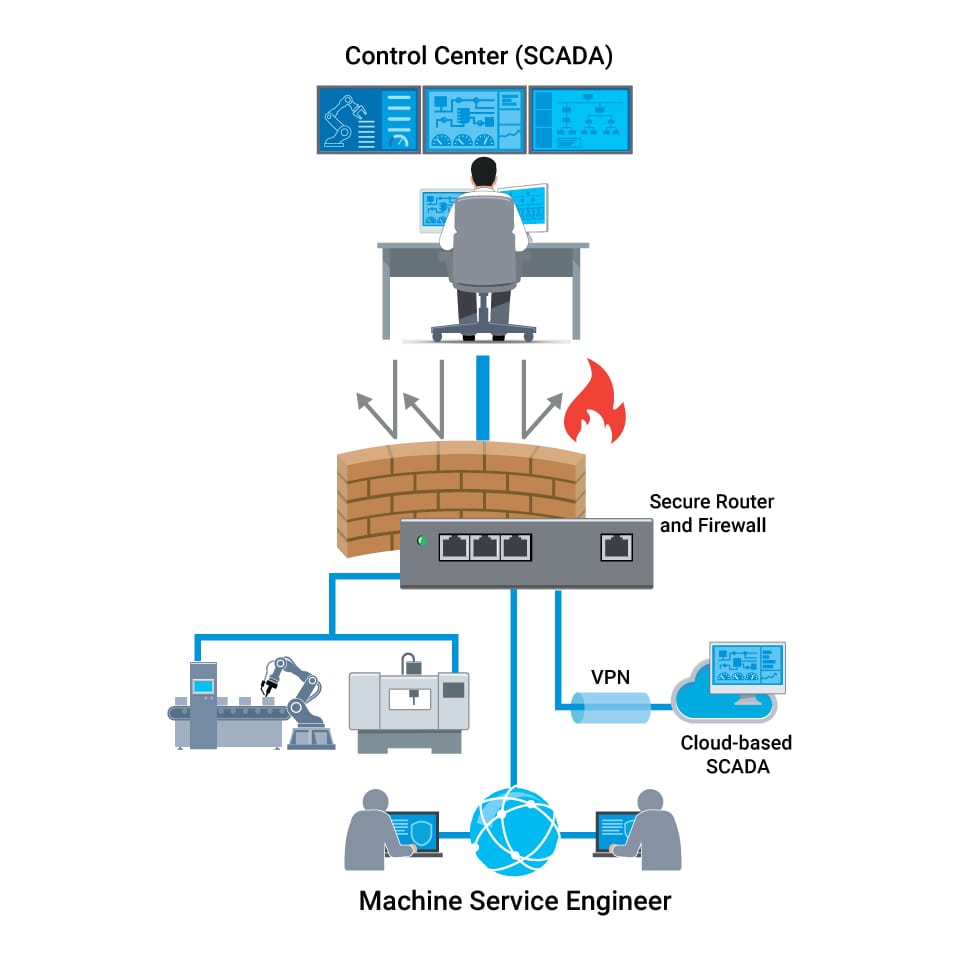
In this light, industrial secure routers and firewalls must go beyond supporting industrial protocol filtering at the command level (read, write, etc.), offering nuanced allow listing control. For heightened security in transmitting sensitive data, contemplate erecting secure tunnels for site-to-site communication. In specific contexts, secure encrypted data transmission is indispensable, especially over public or untrusted networks. In such scenarios, factoring in VPN capability while selecting industrial secure routers and firewalls is essential.
Key Criteria 3
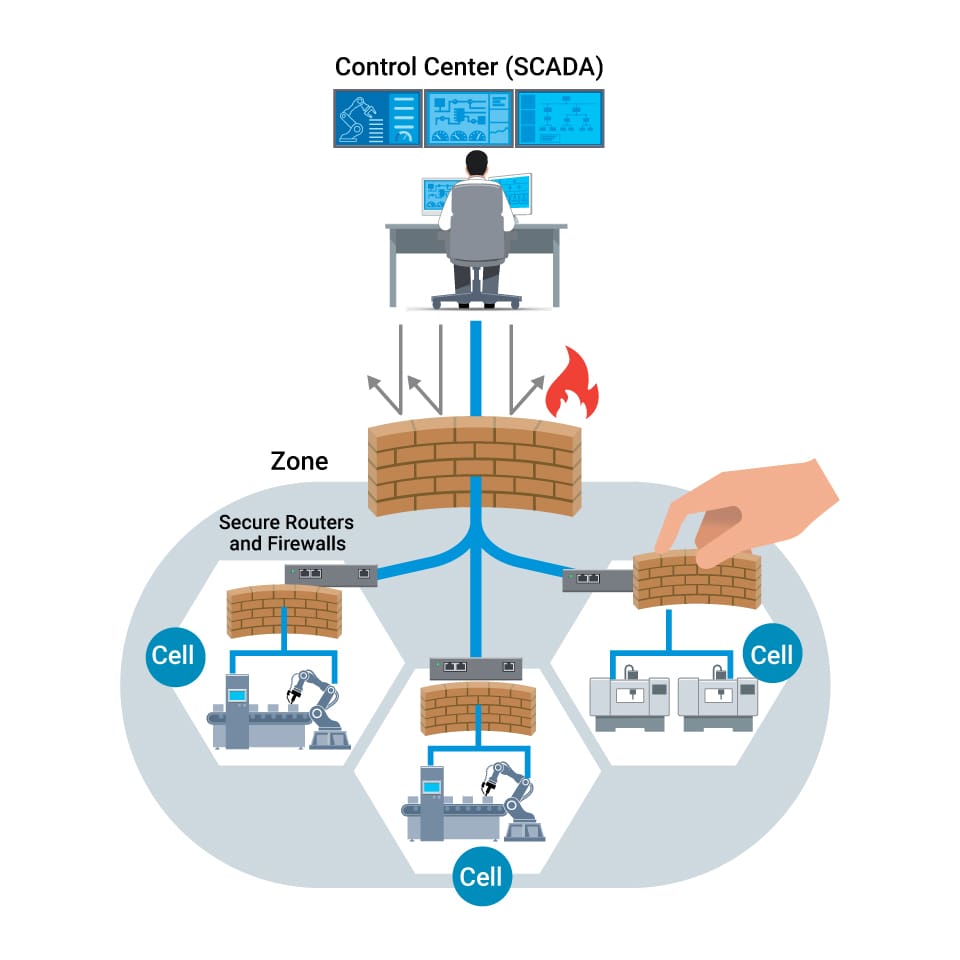
Mastering Your Network with Firewalls and Order
In industrial realms, the deployment of
firewalls to oversee data traffic and safeguard field equipment from malicious
assaults can reach considerable numbers – potentially hundreds or thousands.
This might entail an even larger tally of IP addresses on your network. As
networks undergo expansion, managing devices, firewall rules, and IP addresses
becomes progressively intricate. Here, Network Address Translation (NAT) emerges
as a pivotal player when deploying industrial secure routers and firewalls.
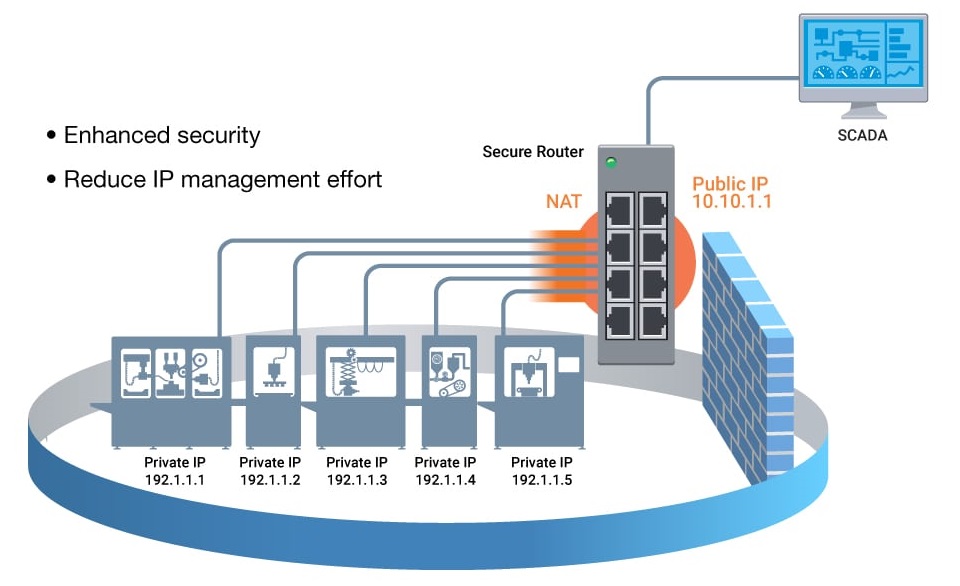
NAT
functions as a crucial tool, permitting the reuse of machine IP address schemes
within the same network. This approach facilitates the connection of multiple
devices to the Internet using a reduced count of IP addresses. This practice
significantly curtails maintenance tasks, and administrative demands and
concurrently supports straightforward network segmentation. Furthermore, NAT
bolsters security for private networks by preserving internal addressing away
from external exposure.
Selecting the right secure router or
firewall for your application constitutes the initial phase in bolstering
industrial network security. Employing these three criteria can eliminate some
uncertainty. For instance, the Moxa EDR-810 Series, a comprehensively
integrated industrial multiport secure router with firewall/NAT/VPN and managed Layer 2 switch functionalities, could offer a comprehensive solution.
Ultimately, your chosen solution should seamlessly align with your precise
application prerequisites.
Constructing robust industrial networks pivots on two
essential pillars: network segmentation and traffic filtering.


